ନନ୍ଦ ବଂଶ
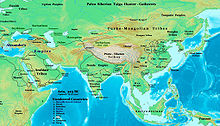
ନନ୍ଦ ରାଜବଂଶ, ଖ୍ରୀଷ୍ଟପୂର୍ବ ଚତୁର୍ଥ ଶତାବ୍ଦୀ ପ୍ରାଚୀନ ଭାରତର ମଗଧ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରୁ ଉପତ୍ତି ହୋଇ ତାହା ଖ୍ରୀଷ୍ଟପୂର୍ବ ୩୪୫-୩୨୧ ଯାଏ ରାଜୁତି କରିଥିବାର ତଥ୍ୟ ରହିଛି । ଶିଖର ସମୟରେ ଏହା ପୂର୍ବ ଭାରତର ବଙ୍ଗଠାରୁ ଉତ୍ତରରେ ପଞ୍ଜାବ ଅଞ୍ଚଳ ଓ ଦକ୍ଷିଣରେ ବିନ୍ଧ୍ୟ ପର୍ବତମାଳା ପର୍ଯ୍ୟନ୍ତ ବ୍ୟାପ୍ତ ଥିଲା । .[୧] ଏହି ବଂଶର ରାଜାମାନେ ଖୁବ ବିତ୍ତଶାଳୀ ଥିଲେ ।ପରେ ଚନ୍ଦ୍ରଗୁପ୍ତ ମୌର୍ଯ୍ୟ ନନ୍ଦ ସମ୍ରାଟଙ୍କୁ ପରାଜିତ କରି ମୌର୍ଯ୍ୟ ସାମ୍ଭ୍ରାଜ୍ୟର ସ୍ଥାପନା କରିଥିଲେ ।
ନନ୍ଦା ରାଜବଂଶର ସ୍ଥାପନା
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]ପୂରାଣ ବର୍ଣିତ 'ମହାପ୍ରସାଦ ନନ୍ଦ , ଯାହାଙ୍କୁ ' କ୍ଷ୍ଯାତ୍ରିୟମାନଙ୍କ ବିନାଶକାରୀ' ଆଖ୍ୟା ଦିଅ ଯାଇଥିଲା , ପାଞ୍ଚାଳ , କାଶୀ , କଳିଙ୍ଗ , ଅସ୍ମକ, କୁରୁ , ମୈଥିଲା , ସୁରସେନା , ବିତିହୋତ୍ର ଆଦି ରାଜ୍ୟ ଜୟ କରି ନନ୍ଦ ସମ୍ଭ୍ରାଜ୍ୟର ଅବତାରଣା କରିଥିଲେ । [୨]ସେ ତାଙ୍କ ସମ୍ଭ୍ରାଜ୍ୟର ବିସ୍ତାର କରି ଦକ୍ଷିଣରେ ବିନ୍ଧ୍ୟ ପର୍ବତାଞ୍ଚଳ ଓ ଡେକାନ ଅବବାହିକା ମଧ୍ୟ ଅକ୍ତିଆର କରିଥିଲେ । [୩][୪][୫]ଖୃଷ୍ଟପୂର୍ବ ୩୪୫ ମସିହାରେ ନନ୍ଦ ରାଜା ଶିଶୁନାଗ ରାଜବଂଶର ସାମ୍ଭ୍ରାଜ୍ୟ କୁ ମଧ୍ୟ ନିଜ ଅକ୍ତିଆରକୁ ନେଇଯାଇଥିଲେ ।
ସାମରିକ ଶକ୍ତି
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]ହରୟାଙ୍କ ଓ ଶିଶୁନାଗ ସମ୍ଭ୍ରାଜ୍ୟ ଏକ ବିଶାଳ ଉତ୍ତର ଭାରତ ସମ୍ଭ୍ରାଜ୍ୟ ସ୍ଥାପନର ଯେଉଁ ମୂଳଦୁଆ ପକେଇଥିଲେ , ନନ୍ଦ ରାଜାମାନେ ତାହାକୁ ହିଁ ସାକାର କରିବାକୁ ଯୋଜନା କରିଥିଲେ । .[୬] ଏହା ହାସଲ କରିବାକୁ ସେମାନେ ଏକ ବିଶାଳ ସେନା ବାହିନୀ ଗଠନ କରିଥିଲେ , ଯହିଁରେ ୨୦,୦୦୦ ଘୋଡ଼ା ସବାର ସୈନ୍ୟ ସହ ୨,୦୦,୦୦୦ ସମୁଦାୟ ବାହିନୀ , ୨୦୦୦ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ରଥ ଓ ୩,୦୦୦ ଯୁଦ୍ଧହ ହସ୍ତୀ ରଖିଥିଲେ । .[୭][୮] ଗ୍ରୀକ ଇତିହାସ ବିଶାରଦ ପ୍ଳୁତର୍ଚଙ୍କ ମତରେ ନନ୍ଦା ରାଜାଙ୍କ ସେନା ବାହିନୀର ସମୁଦାୟ ସଂଖ୍ୟା ୨,୦୦,୦୦୦ , ଯହିଁରେ ୮୦,୦୦୦ ଘୋଡ଼ା ସବାର ସୈନ୍ୟ ,୮,୦୦୦ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ରଥ , ୬,୦୦୦ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ ହସ୍ତୀ ସାମିଲ ଥିଲେ । .[୭][୯] କିନ୍ତୁ ନନ୍ଦଙ୍କ ସେନା ଆଲେକଜାଣ୍ଡାରଙ୍କ ସେନା ସହ ଯୁଦ୍ଧ କରିବାର ଅବସର ପାଇନଥିଲେ । ଆଲେକଜାଣ୍ଡାର ଉତ୍ତର ପଶ୍ଚିମ ଭାରତର ସମତଳ ଅଞ୍ଚଳରେ ନିଜକୁ ସୀମିତ ରଖିଥିଲେ । କାରଣ ତାଙ୍କ ସେନା ବିଅସ ନଦୀ ତଟରେ ପହଞ୍ଚିବା ପରେ ଆଉ ଆଗକୁ ଯାଇ ନନ୍ଦଙ୍କ ୪,୦୦୦ ସୁପ୍ରସ୍ତୁତ ସେନାକୁ ସମ୍ମୁଖୀନ ହେବାକୁ ଅମଙ୍ଗ ହେଇ ବିଦ୍ରୋହ କଲେ । .[୭][୧୦]
ହାତିଗୁମ୍ଫାର ସିଲାଲେଖଦ୍ୱାରା ନନ୍ଦ ସମ୍ଭ୍ରାଜ୍ୟ କଳିଙ୍ଗ ରାଜ୍ୟକୁ ମଧ୍ୟ କରାଗତ କରିଥିବାର ପ୍ରମାଣ ଦିଏ। .[୬]
ନନ୍ଦଙ୍କ ସମ୍ପଦ ଓ କାର୍ଜ୍ୟାବଳି
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]ଅମାପ ସମ୍ପତ୍ତିର ଅଧିକାରୀ ଥିବା ନନ୍ଦ ରାଜାମାନେ ଜନସେଚନ ସୁବିଧା , ନିୟନ୍ତ୍ରିତ ବାଣିଜ୍ୟ ପରି ଲୋକ ହିତକର କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟ କରିଥିଲେ । ଶାସନ କାର୍ଯ୍ୟ ମଧ୍ୟ ଶୃଙ୍ଖଳିତ କରିବା ପାଇଁ ଅନେକ ମନ୍ତ୍ରୀଙ୍କୁ ନିଯୁକ୍ତି ଦେଇଥିଲେ । .[୨] ତେବେ ଅତ୍ୟଧିକ ଟିକସ ଅସୁଲି ପାଇଁ ନନ୍ଦ ରାଜାମାନେ ଅପ୍ରିୟ ହେଇ ପଡିଥିଲେ । .[୨]
ସାହିତ୍ୟରେ ନନ୍ଦ
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]କଥାସାରିତସାଗରରେ ନନ୍ଦ ରାଜୁତି ବିଷୟରେ ଉଲ୍ଲେଖ ଅଛି । [୧୧]
Notes
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]- ↑ Radha Kumud Mookerji, Chandragupta Maurya and His Times, 4th ed.
- ↑ ୨.୦ ୨.୧ ୨.୨ Kalinga (India) formed part of the Nanda Empire but subsequently broke free until it was re-conquered by Ashoka Maurya, c. 260 BCE.
- ↑ http://www.forumancientcoins.com/india/earliest/nanda.html
- ↑ https://books.google.com/books?id=f1XMtc2Q97IC&pg=PA28
- ↑ Kumar, Raj (2008). Encyclopaedia of untouchables ancient, medieval and modern. Delhi: Kalpaz Publications. p. 151. ISBN 8178356643.
- ↑ ୬.୦ ୬.୧ Singh 2008, p. 273.
- ↑ ୭.୦ ୭.୧ ୭.୨ Sastri 1988, p. 16.
- ↑ Gabriel, Richard A. (30 November 2002), The great armies of antiquity (1.udg. ed.), Westport, Conn. [u.a.]: Praeger, ISBN 9780275978099
{{citation}}: More than one of|ISBN=and|isbn=specified (help) - ↑ (Raychaudhuri & Mukherjee 1996, pp. 204-210)
- ↑ Kaushik, Roy (2015), Military Manpower, Armies and Warfare in South Asia "Warfare, Society and Culture", Routledge, ISBN 1317321286
{{citation}}: More than one of|ISBN=and|isbn=specified (help) - ↑ Sastri 1988, p. 17.
ଆଧାର
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]- Singh, Upinder (2008), A history of ancient and early medieval India : from the Stone Age to the 12th century, New Delhi: Pearson Longman, ISBN 978-81-317-1120-0
{{citation}}: More than one of|ISBN=and|isbn=specified (help) - Raychaudhuri, H. C.; Mukherjee, B. N. (1996). Political History of Ancient India: From the Accession of Parikshit to the Extinction of the Gupta Dynasty. Oxford University Press.
- Sastri, K. A. Nilakanta, ed. (1988), Age of the Nandas and Mauryas (Second ed.), Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 81-208-0465-1
{{citation}}: More than one of|ISBN=and|isbn=specified (help)
| Middle kingdoms of India | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timeline and
cultural period |
Northwestern India
(Punjab-Sapta Sindhu) |
Indo-Gangetic Plain | Central India | Southern India | ||
| Western Gangetic Plain
(Kuru-Panchala) |
Northern India
(Central Gangetic Plain) |
Northeastern India
(Northeast India) | ||||
| IRON AGE | ||||||
| Culture | Late Vedic Period | Late Vedic Period
(Brahmin ideology)[a] Painted Grey Ware culture |
Late Vedic Period
(Kshatriya/Shramanic culture)[b] Northern Black Polished Ware |
Pre-history | ||
| 6th century BC | Gandhara | Kuru-Panchala | Magadha | Adivasi (tribes) | ||
| Culture | Persian-Greek influences | "Second Urbanisation"
Rise of Shramana movements Jainism - Buddhism - Ājīvika - Yoga |
Pre-history | |||
| 5th century BC | (Persian rule) | Shishunaga dynasty | Adivasi (tribes) | |||
| 4th century BC | (Greek conquests) |
Nanda empire Kalinga | ||||
| HISTORICAL AGE | ||||||
| Culture | Spread of Buddhism | Pre-history | Sangam period (300 BC – 200 AD) | |||
| 3rd century BC | Maurya Empire | Early Cholas
Early Pandyan Kingdom Satavahana dynasty Cheras 46 other small kingdoms in Ancient Thamizhagam | ||||
| Culture | Preclassical Hinduism[c] - "Hindu Synthesis"[d] (ca. 200 BC - 300 AD)[e][f] Epics - Puranas - Ramayana - Mahabharata - Bhagavad Gita - Brahma Sutras - Smarta Tradition |
Sangam period
(continued) | ||||
| 2nd century BC | Indo-Greek Kingdom | Shunga Empire | Adivasi (tribes) | Early Cholas
Early Pandyan Kingdom Satavahana dynasty Cheras 46 other small kingdoms in Ancient Thamizhagam | ||
| 1st century BC | Yona | Maha-Meghavahana Dynasty | ||||
| 1st century AD |
Indo-Scythians Indo-Parthians |
Kuninda Kingdom | ||||
| 2nd century | Pahlava | Varman dynasty | ||||
| 3rd century | Kushan Empire | Western Satraps | Kamarupa kingdom | Kalabhra dynasty
Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | ||
| Culture | "Golden Age of Hinduism"(ca. AD 320-650)[g] Puranas | |||||
| 4th century | Gupta Empire | Kalabhra dynasty
Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) Kadamba Dynasty Western Ganga Dynasty | ||||
| 5th century | Maitraka | Adivasi (tribes) | Kalabhra dynasty
Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) Vishnukundina | |||
| 6th century | Kalabhra dynasty
Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras) | |||||
| Culture | Late-Classical Hinduism (ca. AD 650-1100)[h] Advaita Vedanta - Tantra | |||||
| 7th century | Indo-Sassanids | Vakataka dynasty Empire of Harsha |
Mlechchha dynasty | Adivasi (tribes) | Pandyan Kingdom(Under Kalabhras)
Pandyan Kingdom(Revival) Pallava | |
| 8th century | Kidarite Kingdom | Pandyan Kingdom
Kalachuri | ||||
| 9th century | Indo-Hephthalites (Huna) | Gurjara-Pratihara | Pandyan Kingdom
Medieval Cholas Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Chalukya Chera Perumals of Makkotai | |||
| 10th century | Pala dynasty
Kamboja-Pala dynasty |
Medieval Cholas
Pandyan Kingdom(Under Cholas) Chera Perumals of Makkotai Rashtrakuta | ||||
References and sources for table References Sources
| ||||||
