ମହିଳା ନୋବେଲ ପୁରସ୍କାର ବିଜେତା
ଦେଖଣା
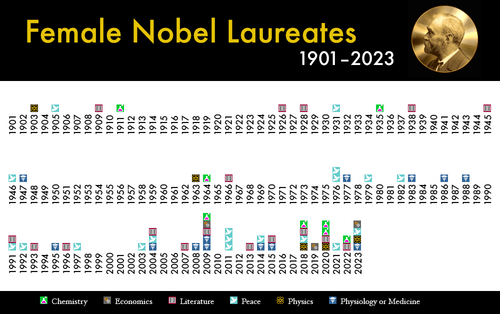
ବିଶ୍ୱରେ ପ୍ରତିଭା ସମ୍ପନ୍ନ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିମାନଙ୍କୁ ଯେତେଗୁଡିଏ ପୁରସ୍କାର ଦିଆଯିବାର ବ୍ୟବସ୍ଥା ରହିଛି ତନ୍ମଧ୍ୟରେ ନୋବେଲ ପୁରସ୍କାର ହେଉଛି ବିଶ୍ୱର ସର୍ବଶ୍ରେଷ୍ଠ ପୁରସ୍କାର। ଶାନ୍ତି,ଚିକିତ୍ସା,ସାହିତ୍ୟ,ପଦାର୍ଥ ବିଜ୍ଞାନ,ରସାୟନ ବିଜ୍ଞାନ ଏବଂ ଅର୍ଥନୀତି କ୍ଷେତ୍ରରେ ଯେ କୈଣସି ଦେଶ ଓ ଜାତିର ଯୋଗ୍ୟବିବେଚିତ ବ୍ୟକ୍ତିଙ୍କୁ ଏହି ବାର୍ଷିକ ପୁରସ୍କାର ଦିଆଯାଏ। ପ୍ରଥମ ମହିଳା ନୋବେଲ ବିଜେତା ମେରୀ କ୍ୟୁରୀ ଥିଲେ ଏବେ ୨୦୧୫ ମସିହାରେ ମଲାଲା ୟୁସୂଫଜୈ ପାଇଛନ୍ତି।
ବିଜେତା
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]| Year | Image | Laureate | Country | Category | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 
|
Marie Skłodowska-Curie (shared with Pierre Curie and Henri Becquerel) |
Poland and France | Physics | "in recognition of the extraordinary services they have rendered by their joint researches on the radiation phenomena discovered by Professor Henri Becquerel"[୧] |
| 1905 | 
|
Bertha von Suttner | Austria–Hungary | Peace | Honorary President of Permanent International Peace Bureau, Bern, Switzerland; Author of Lay Down Your Arms.[୨] |
| 1909 | 
|
Selma Lagerlöf | Sweden | Literature | "in appreciation of the lofty idealism, vivid imagination and spiritual perception that characterize her writings"[୩] |
| 1911 | 
|
Marie Curie-Skłodowska | Poland and France | Chemistry | "for her discovery of radium and polonium"[୪] |
| 1926 | 
|
Grazia Deledda | Italy | Literature | "for her idealistically inspired writings which with plastic clarity picture the life on her native island and with depth and sympathy deal with human problems in general"[୫] |
| 1928 | 
|
Sigrid Undset | Norway | Literature | "principally for her powerful descriptions of Northern life during the Middle Ages"[୬] |
| 1931 | 
|
Jane Addams (shared with Nicholas Murray Butler) |
United States | Peace | Sociologist; International President, Women's International League for Peace and Freedom.[୭] |
| 1935 | 
|
Irène Joliot-Curie (shared with Frédéric Joliot-Curie) |
France | Chemistry | "for their synthesis of new radioactive elements"[୮] |
| 1938 | 
|
Pearl S. Buck | United States | Literature | "for her rich and truly epic descriptions of peasant life in China and for her biographical masterpieces"[୯] |
| 1945 | 
|
Gabriela Mistral | Chile | Literature | "for her lyric poetry which, inspired by powerful emotions, has made her name a symbol of the idealistic aspirations of the entire Latin American world"[୧୦] |
| 1946 | 
|
Emily Greene Balch (shared with John Raleigh Mott) |
United States | Peace | Formerly Professor of History and Sociology; Honorary International President, Women's International League for Peace and Freedom.[୧୧] |
| 1947 | 
|
Gerty Theresa Cori (shared with Carl Ferdinand Cori and Bernardo Houssay) |
United States | Physiology or Medicine | "for their discovery of the course of the catalytic conversion of glycogen"[୧୨] |
| 1963 | 
|
Maria Goeppert-Mayer (shared with J. Hans D. Jensen and Eugene Wigner) |
United States | Physics | "for their discoveries concerning nuclear shell structure"[୧୩] |
| 1964 | ଫାଇଲ:Dorothy Hodgkin Nobel.jpg | Dorothy Crowfoot Hodgkin | United Kingdom | Chemistry | "for her determinations by X-ray techniques of the structures of important biochemical substances"[୧୪] |
| 1966 | 
|
Nelly Sachs (shared with Samuel Agnon) |
Sweden and Germany | Literature | "for her outstanding lyrical and dramatic writing, which interprets Israel's destiny with touching strength"[୧୫] |
| 1976 | 
|
Betty Williams | United Kingdom | Peace | Founder of the Northern Ireland Peace Movement (later renamed Community of Peace People)[୧୬] |

|
Mairead Corrigan | ||||
| 1977 | 
|
Rosalyn Sussman Yalow (shared with Roger Guillemin and Andrew Schally) |
United States | Physiology or Medicine | "for the development of radioimmunoassays of peptide hormones"[୧୭] |
| 1979 | 
|
Mother Teresa | India and Yugoslavia |
Peace | Leader of Missionaries of Charity, Calcutta.[୧୮] |
| 1982 | 
|
Alva Myrdal (shared with Alfonso García Robles) |
Sweden | Peace | Former Cabinet Minister; Diplomat; Writer.[୧୯] |
| 1983 | 
|
Barbara McClintock | United States | Physiology or Medicine | "for her discovery of mobile genetic elements"[୨୦] |
| 1986 | 
|
Rita Levi-Montalcini (shared with Stanley Cohen) |
Italy and United States |
Physiology or Medicine | "for their discoveries of growth factors"[୨୧] |
| 1988 | 
|
Gertrude B. Elion (shared with James W. Black and George H. Hitchings) |
United States | Physiology or Medicine | "for their discoveries of important principles for drug treatment"[୨୨] |
| 1991 | 
|
Nadine Gordimer | South Africa | Literature | "who through her magnificent epic writing has - in the words of Alfred Nobel - been of very great benefit to humanity"[୨୩] |

|
Aung San Suu Kyi | Burma | Peace | "for her non-violent struggle for democracy and human rights"[୨୪] | |
| 1992 | 
|
Rigoberta Menchú | Guatemala | Peace | "in recognition of her work for social justice and ethno-cultural reconciliation based on respect for the rights of indigenous peoples"[୨୫] |
| 1993 | 
|
Toni Morrison | United States | Literature | "who in novels characterized by visionary force and poetic import, gives life to an essential aspect of American reality"[୨୬] |
| 1995 | 
|
Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard (shared with Edward B. Lewis and Eric F. Wieschaus) |
Germany | Physiology or Medicine | "for their discoveries concerning the genetic control of early embryonic development"[୨୭] |
| 1996 | 
|
Wisława Szymborska | Poland | Literature | "for poetry that with ironic precision allows the historical and biological context to come to light in fragments of human reality"[୨୮] |
| 1997 | 
|
Jody Williams (shared with the International Campaign to Ban Landmines) |
United States | Peace | "for their work for the banning and clearing of anti-personnel mines"[୨୯] |
| 2003 | 
|
Shirin Ebadi | Iran | Peace | "for her efforts for democracy and human rights. She has focused especially on the struggle for the rights of women and children"[୩୦] |
| 2004 | 
|
Elfriede Jelinek | Austria | Literature | "for her musical flow of voices and counter-voices in novels and plays that with extraordinary linguistic zeal reveal the absurdity of society's clichés and their subjugating power"[୩୧] |

|
Wangari Maathai | Kenya | Peace | "for her contribution to sustainable development, democracy and peace"[୩୨] | |

|
Linda B. Buck (shared with Richard Axel) |
United States | Physiology or Medicine | "for their discoveries of odorant receptors and the organization of the olfactory system"[୩୩] | |
| 2007 | 
|
Doris Lessing | United Kingdom | Literature | "that epicist of the female experience, who with scepticism, fire and visionary power has subjected a divided civilisation to scrutiny"[୩୪] |
| 2008 | 
|
Françoise Barré-Sinoussi (shared with Harald zur Hausen and Luc Montagnier) |
France | Physiology or Medicine | "for their discovery of HIV, human immunodeficiency virus"[୩୫] |
| 2009 | 
|
Elizabeth Blackburn (shared with Jack W. Szostak) |
Australia and United States | Physiology or Medicine | "for the discovery of how chromosomes are protected by telomeres and the enzyme telomerase"[୩୬] |

|
Carol W. Greider (shared with Jack W. Szostak) |
United States | |||

|
Ada E. Yonath (shared with Venkatraman Ramakrishnan and Thomas A. Steitz) |
Israel | Chemistry | "for studies of the structure and function of the ribosome"[୩୭] | |

|
Herta Müller | Germany and Romania | Literature | "who, with the concentration of poetry and the frankness of prose, depicts the landscape of the dispossessed"[୩୮] | |

|
Elinor Ostrom (shared with Oliver E. Williamson) |
United States | Economics | "for her analysis of economic governance, especially the commons"[୩୯] | |
| 2011 | 
|
Ellen Johnson Sirleaf | Liberia | Peace | "For their non-violent struggle for the safety of women and for women's rights to full participation in peace-building work"[୪୦] |

|
Leymah Gbowee | ||||

|
Tawakel Karman | Yemen | |||
| 2013 | Alice Munro | Canada | Literature | "master of the contemporary short story"[୪୧] | |
| 2014 | May-Britt Moser (shared with Edvard Moser and John O'Keefe) |
Norway | Physiology or Medicine | "for their discoveries of cells that constitute a positioning system in the brain"[୪୨] | |

|
Malala Yousafzai (shared with Kailash Satyarthi) |
Pakistan | Peace | "for their struggle against the suppression of children and young people and for the right of all children to education".[୪୩] | |
| 2015 | 
|
Tu Youyou (shared with William C. Campbell and Satoshi Ōmura) |
China | Physiology or Medicine | "for her discoveries concerning a novel therapy against Malaria (artemisinin)"[୪୪] |

|
Svetlana Alexievich | Belarus | Literature | "for her polyphonic writings, a monument to suffering and courage in our time"[୪୫] | |
| 2018 | 
|
Donna Strickland (shared with Gérard Mourou and Arthur Ashkin) |
Canada | Physics | "for their method of generating high-intensity, ultra-short optical pulses"[୪୬] |

|
Frances Arnold (shared with Gregory Winter and George Smith) |
United States | Chemistry | "for the directed evolution of enzymes"[୪୭] | |

|
Nadia Murad (shared with Denis Mukwege) |
Iraq | Peace | "for their efforts to end the use of sexual violence as a weapon of war and armed conflict"[୪୮] | |

|
Olga Tokarczuk | Poland | Literature | "for a narrative imagination that with encyclopedic passion represents the crossing of boundaries as a form of life"[୪୯] | |
| 2019 | Esther Duflo (shared with Abhijit Banerjee and Michael Kremer) |
France and United States | Economics | "for their experimental approach to alleviating global poverty"[୫୦] | |
| 2020 | Andrea M. Ghez (shared with Reinhard Genzel and Roger Penrose) |
United States | Physics | "for the discovery of a supermassive compact object at the centre of our galaxy"[୫୧] | |

|
Emmanuelle Charpentier (shared with Jennifer Doudna) |
France | Chemistry | "for the development of a method for genome editing"[୫୨] | |

|
Jennifer Doudna (shared with Emmanuelle Charpentier) |
United States | Chemistry | "for the development of a method for genome editing"[୫୩] | |

|
Louise Glück | United States | Literature | "for her unmistakable poetic voice that with austere beauty makes individual existence universal"[୫୪] |
ଆଧାର
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]- ↑ ଆଧାର ଭୁଲ: ଅଚଳ
<ref>ଚିହ୍ନ;Physics1903ନାମରେ ଥିବା ଆଧାର ଭିତରେ କିଛି ଲେଖା ନାହିଁ । - ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize 1905". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 1909". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1911". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 1926". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 1928". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize 1931". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1935". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 1938". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 1945". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize 1946". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1947". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "The Nobel Prize in Physics 1963". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1964". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 1966". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize 1976". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1977". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize 1979". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize 1982". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1983". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1986". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1988". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 1991". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize 1991". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize 1992". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 1993". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1995". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 1996". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize 1997". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2012-09-09.
- ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize 2003". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 2004". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize 2004". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2004". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 2007". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2008". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2008-10-16.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2009". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2009-10-05.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2009". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2009-10-07.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 2009". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2009-10-08.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Economics 2009". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2009-10-12.
- ↑ "The Nobel Peace Prize 2011". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2011-10-07.
- ↑ "The Nobel Prize in Literature 2013" (PDF). Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2013-10-10.
- ↑ "The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2014". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2014-10-07.
- ↑ "The Nobel Peace Prize 2014" (PDF). Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2014-10-10.
- ↑ "The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2015" (PDF). Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2015-10-05.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 2015". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 8 October 2015.
- ↑ "The Nobel Prize in Physics 2018". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 13 October 2018.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Chemistry Is Awarded to 3 Scientists for Using Evolution in Design of Molecules". Retrieved 3 October 2018.
- ↑ "Nobel Peace Prize for anti-rape activists Nadia Murad and Denis Mukwege". Retrieved 5 October 2018.
- ↑ "Nobel Prize in Literature 2018". Nobel Foundation. Retrieved 2019-10-10.
- ↑ Nobel Prize 2019 nobelprize.org
- ↑ Nobel Prize 2020 nobelprize.org
- ↑ name="Nobel Chemistry Prize 2020" nobelprize.org
- ↑ name="Nobel Chemistry Prize 2020"nobelprize.org
- ↑ "Summary of the 2020 Nobel Prize in Literature".



