ଟନସିଲେକ୍ଟୋମି
| ଟନସିଲେକ୍ଟୋମି | |
|---|---|
| ହସ୍ତକ୍ଷେପ | |
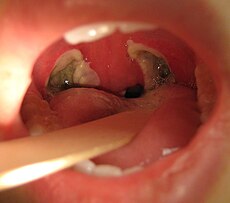 ଟନସିଲେକ୍ଟୋମି ଅପରେଶନର ୩ ଦିନ ପରେ ଗଳା ପଛ ପାଖର ଦୃଶ୍ୟ । | |
| ICD-9-CM | ଛାଞ୍ଚ:ICD9proc-ଛାଞ୍ଚ:ICD9proc |
| MeSH | D014068 |
| MedlinePlus | 003013 |
ଟନସିଲେକ୍ଟୋମି (ଇଂରାଜୀ ଭାଷାରେ Tonsillectomy) ଏକ ଅସ୍ତ୍ରୋପଚାର ବା ଅପରେଶନ (surgical procedure) ଯେଉଁଥିରେ ଗଳାରେ ଥିବା ପାଲାଟାଇନ ଟନସିଲଦ୍ୱୟ (palatine tonsil) ସମ୍ପୁର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଭାବରେ ବାହାର କରିଦିଆଯାଏ ।[୧] ଏହି ଅପରେଶନ ମୂଖ୍ୟତଃ ଗଳା ସଂକ୍ରମଣ (throat infections) ଓ ଅବସ୍ଟ୍ରକ୍ଟିଭ ସ୍ଲିପ ଆପନିଆ (ଓଏସଏ) (obstructive sleep apnea ବା OSA) ରୋଗ ନିମନ୍ତେ କରାଯାଏ ।[୧] ବାରମ୍ବାର ଗଳା ସଂକ୍ରମଣ ଥିବା ରୋଗୀଙ୍କର ଅପରେଶନ ପରେ ୨/୩ ବର୍ଷ ପାଇଁ ଅଳ୍ପ ସଂକ୍ରମଣ ହୁଏ କିନ୍ତୁ ଦୀର୍ଘକାଳୀନ ଉପକାର ବିଷୟ ସ୍ପଷ୍ଟ ହୋଇନାହିଁ । [୧][୨] ଓଏସଏ ରୋଗରେ ଜୀବନଚର୍ଯ୍ୟାରେ (quality of life) ଉନ୍ନତି ଘଟେ । [୩]
ଅପରେଶନ ପରବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ସମୟରେ ବାନ୍ତି, ଖାଇବା ସମସ୍ୟା, ଗଳା ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା, କଥା କହିବା ସମସ୍ୟା ଓ ରକ୍ତସ୍ରାବ ହୋଇପାରେ । [୧] ଅପରେଶନର ଏକ ଦିନ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ଓ ତା'ପରେ ଦୁଇ ଦିନ ମଧ୍ୟରେ ରକ୍ତସ୍ରାବ ହୋଇପାରେ । [୧] ଫଳରେ ପ୍ରାୟ ୨,୩୬୦ ଅପରେଶନ ପରେ ଜଣକର ମୃତ୍ୟୁ ହୋଇପାରେ ।[୧] ଅପରେଶନ ପରବର୍ତ୍ତୀ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରଣା ଲାଘବ ନିମନ୍ତେ ଆଇବୁପ୍ରୋଫେନ୍ ଓ ପାରାସେଟାମୋଲ ଦିଆଯାଇପାରେ ।[୧] ଧାତୁ ଯନ୍ତ୍ରପାତି (metal instruments) ବା ଇଲେକ୍ରୋକଟେରି (electrocautery) ସାହାଯ୍ୟରେ ଅପରେଶନ କରାଯାଏ ।[୧][୪] ଟନସିଲ ସହିତ ଆଡେନଏଡ (adenoid) ବାହାର କରିବା ଅପରେଶନକୁ ଆଡେନୋଟନସିଲେକ୍ଟୋମି କୁହାଯାଏ । [୧]
ଏହି ଅପରେଶନର ବର୍ଣ୍ଣନା ସନ ୦୦୫୦ରେ ସେଲସସ୍ (Celsus) କରିଥିଲେ ।[୫] ସନ ୨୦୧୦ରେ ସନ ୧୯୭୦ ଅପେକ୍ଷା କମ୍ ଅପରେଶନ ହେଉଥିଲା କିନ୍ତୁ ବାହ୍ୟ ରୋଗୀ ବିଭାଗରେ ଏହା ଦ୍ୱିତୀୟ ସର୍ବାଧିକ ସଂଖ୍ୟକ ଅପରେଶନ ଥିଲା ।[୧] ସନ ୨୦୧୩ରେ ଡାକ୍ତରଖାନାରେ ଆଡମିଶନ ହୋଇଥିବା ରୋଗୀଙ୍କୁ ଏହି ଅପରେଶନ ନିମନ୍ତେ ଯୁକ୍ତରାଷ୍ଟ୍ର ଆମେରିକାରେ ୪,୪୦୦ ଡଲାର ଖର୍ଚ୍ଚ କରିବାକୁ ହେଉଥିଲା ।[୬]
ଆଧାର
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]- ↑ ୧.୦୦ ୧.୦୧ ୧.୦୨ ୧.୦୩ ୧.୦୪ ୧.୦୫ ୧.୦୬ ୧.୦୭ ୧.୦୮ ୧.୦୯ Mitchell, Ron B.; Archer, Sanford M.; Ishman, Stacey L.; Rosenfeld, Richard M.; Coles, Sarah; Finestone, Sandra A.; Friedman, Norman R.; Giordano, Terri; Hildrew, Douglas M.; Kim, Tae W.; Lloyd, Robin M.; Parikh, Sanjay R.; Shulman, Stanford T.; Walner, David L.; Walsh, Sandra A.; Nnacheta, Lorraine C. (5 February 2019). "Clinical Practice Guideline: Tonsillectomy in Children (Update)". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 160 (1_suppl): S1–S42. doi:10.1177/0194599818801757. PMID 30798778.
- ↑ Burton MJ, Glasziou PP, Chong LY, Venekamp RP (November 2014). "Tonsillectomy or adenotonsillectomy versus non-surgical treatment for chronic/recurrent acute tonsillitis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (11): CD001802. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD001802.pub3. PMID 25407135.
Adeno-/tonsillectomy leads to a reduction in the number of episodes of sore throat and days with sore throat in children in the first year after surgery compared to (initial) non-surgical treatment.
- ↑ Venekamp RP, Hearne BJ, Chandrasekharan D, Blackshaw H, Lim J, Schilder AG (October 2015). "Tonsillectomy or adenotonsillectomy versus non-surgical management for obstructive sleep-disordered breathing in children". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (10): CD011165. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011165.pub2. PMID 26465274.
- ↑ Damiani, F; Rada, G; Gana, JC; Brockmann, PE; Alberti, G (2 September 2016). "Long-term effects of adenotonsillectomy in children with obstructive sleep apnoea: protocol for a systematic review". BMJ Open. 6 (9): e010030. doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010030. PMC 5020755. PMID 27591015.
- ↑ Lamprell, L; Ahluwalia, S (April 2015). "Who has been hiding in your tonsillectomy tray? Eponymous instruments in tonsillectomy surgery". The Journal of Laryngology and Otology. 129 (4): 307–13. doi:10.1017/S0022215114003016. PMID 25658777.
- ↑ Sun, GH; Auger, KA; Aliu, O; Patrick, SW; DeMonner, S; Davis, MM (December 2013). "Variation in inpatient tonsillectomy costs within and between US hospitals attributable to postoperative complications". Medical Care. 51 (12): 1048–54. doi:10.1097/MLR.0b013e3182a50325. PMID 23969585.
ବାହ୍ୟ ଲିଙ୍କ
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]- Tonsillectomy Procedures Archived 2008-07-05 at the Wayback Machine.
- History of tonsillectomy
- "Clinical UM Guideline CG-SURG-30: Tonsillectomy for Children". Blue Cross Blue Shield Association of Georgia.
