ଇଲେକ୍ଟ୍ରୋନ
Appearance
| ଏହି ପ୍ରସଙ୍ଗଟି ଅସମ୍ପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ ଅଟେ । ଆପଣ ଏହାକୁ ସଂପୂର୍ଣ୍ଣ କରି ଉଇକିପିଡ଼ିଆକୁ ସମୃଦ୍ଧ କରିପାରିବେ । |
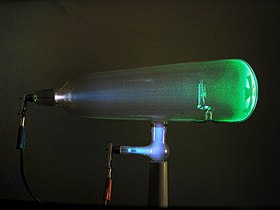 Experiments with a Crookes tube first demonstrated the particle nature of electrons. In this illustration, the profile of the Maltese-cross-shaped target is projected against the tube face at right by a beam of electrons. | |
| ଗଠନ | Elementary particle |
|---|---|
| ପରିସଂଖ୍ୟାନ | Fermionic |
| ପିଢୀ | First |
| ସମ୍ପର୍କ | Gravity, Electromagnetic, Weak |
| ପ୍ରତୀକ | Error no symbol defined, Error no symbol defined |
| ପ୍ରତି-କଣିକା | Positron (also called antielectron) |
| Theorized | Richard Laming (1838–1851), G. Johnstone Stoney (1874) and others. |
| ଆବିଷ୍କାର | J. J. Thomson (1897) |
| ବସ୍ତୁତ୍ଵ | ୯.୧୦୯୩୮୨୯୧(40)×୧୦−୩୧kg ୫.୪୮୫୭୯୯୦୯୪୬(22)×୧୦−୪u [୧,୮୨୨.୮୮୮୪୮୪୫(14)]−1 u ୦.୫୧୦୯୯୮୯୨୮(11)MeV/c2 |
| ବୈଦୁତିକ ଚାର୍ଜ | −୧e −୧.୬୦୨୧୭୬୫୬୫(35)×୧୦−୧୯C −୪.୮୦୩୨୦୪୫୧(10)×୧୦−୧୦esu |
| Magnetic moment | −1.00115965218076(27) μB |
| Spin | 1⁄2 |
ଇଲେକ୍ଟ୍ରୋନ (ପ୍ରତୀକ: e-) ହେଉଛି ବିଯୁକ୍ତାତ୍ମକ ଚାର୍ଜ ବିଶିଷ୍ଟ ଏକ ଅବପରମାଣବିକ କଣିକା ।[୧]
ଇଲେକ୍ଟ୍ରୋନର କୌଣସି ଉପାଦାନ ଥିବା କଥା ଜଣାନାହିଁ । ଏହାକୁ ସାଧାରଣତଃ ପ୍ରାଥମିକ କଣିକା କୁହାଯାଏ । ଗୋଟିଏ ଇଲେକ୍ଟ୍ରୋନର ବସ୍ତୁତ୍ୱ ପ୍ରୋଟୋନ ବସ୍ତୁତ୍ୱର ୧/୧୮୩୬ ଭାଗ ହେଇଥାଏ ।
ଆଧାର
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]- ↑ "JERRY COFF". Retrieved 10 September 2010.
ବାହାର ଲିଙ୍କ
[ସମ୍ପାଦନା]ଉଇକିମିଡ଼ିଆ କମନ୍ସରେ Electrons
ବାବଦରେ ମାଧ୍ୟମ ରହିଛି ।
- "The Discovery of the Electron". American Institute of Physics, Center for History of Physics. Archived from the original on 2008-03-16. Retrieved 2013-06-08.
- "Particle Data Group". University of California.
- Bock, R.K.; Vasilescu, A. (1998). The Particle Detector BriefBook (14th ed.). Springer. ISBN 3-540-64120-3.
- Copeland, Ed. "Spherical Electron". Sixty Symbols. Brady Haran for the University of Nottingham.
